
Added Successfully!

The Cordillera Local Governance Regional Resource Center (CLGRRC) has been established to become a dynamic, interactive, and virtual one-stop shop
for knowledge on local governance. Its primary role is to source, organize, and manage available local governance knowledge and promote its sharing
and use by various stakeholders. It aims to contribute to building the Department of the Interior and Local Government as a knowledge-centric organization
(KCO) and builds learning communities that pursue local governance excellence through knowledge sharing and innovation.
The CLGRRC, through its Sub-LGRRC, caters to the internal and external interested parties of the DILG-CAR including its six (6) provinces, one (1) highly
urbanized city, one (1) component city, seventy-five (75) municipalities, and 1,176 barangays.
As a center for excellence in local governance and as a product of convergence, the CLGRRC is the primary source of information on local governance.
Local government officials and employees, students, researchers, civil society organizations, local resource institutions, and other national line agencies
may find information and answers to their inquiries on local governance in the LGRRC and its website.
Experts in various fields may easily be tapped thru the CLGRRC's Multi- stakeholders Advisory Committee (MSAC). The members of the Committee are
committed to providing technical assistance, information, and other resources to assist the internal and external parties of the CLGRRC.
As the world transitions to the new normal, the CLGRRC is also building up on and strengthening its information and communications technology with
the assistance of the Local Government Academy and the DILG Information Systems and Technology Management Service. This is to address the needs
of its interested parties specifically to ease transactions, improve its knowledge management and implementation of its programs, projects, and activities,
as well as its Quality Management System, and most importantly, to provide the best quality services to its interested parties. The establishment and
upgrading of its facilities are also in keeping up with the current trends and situation and staying relevant as a knowledge-centric organization. The resource
center continues to create linkages with various organizations to advance these gains, explore possible undertakings, and push boundaries to build learning
communities for local governance excellence.
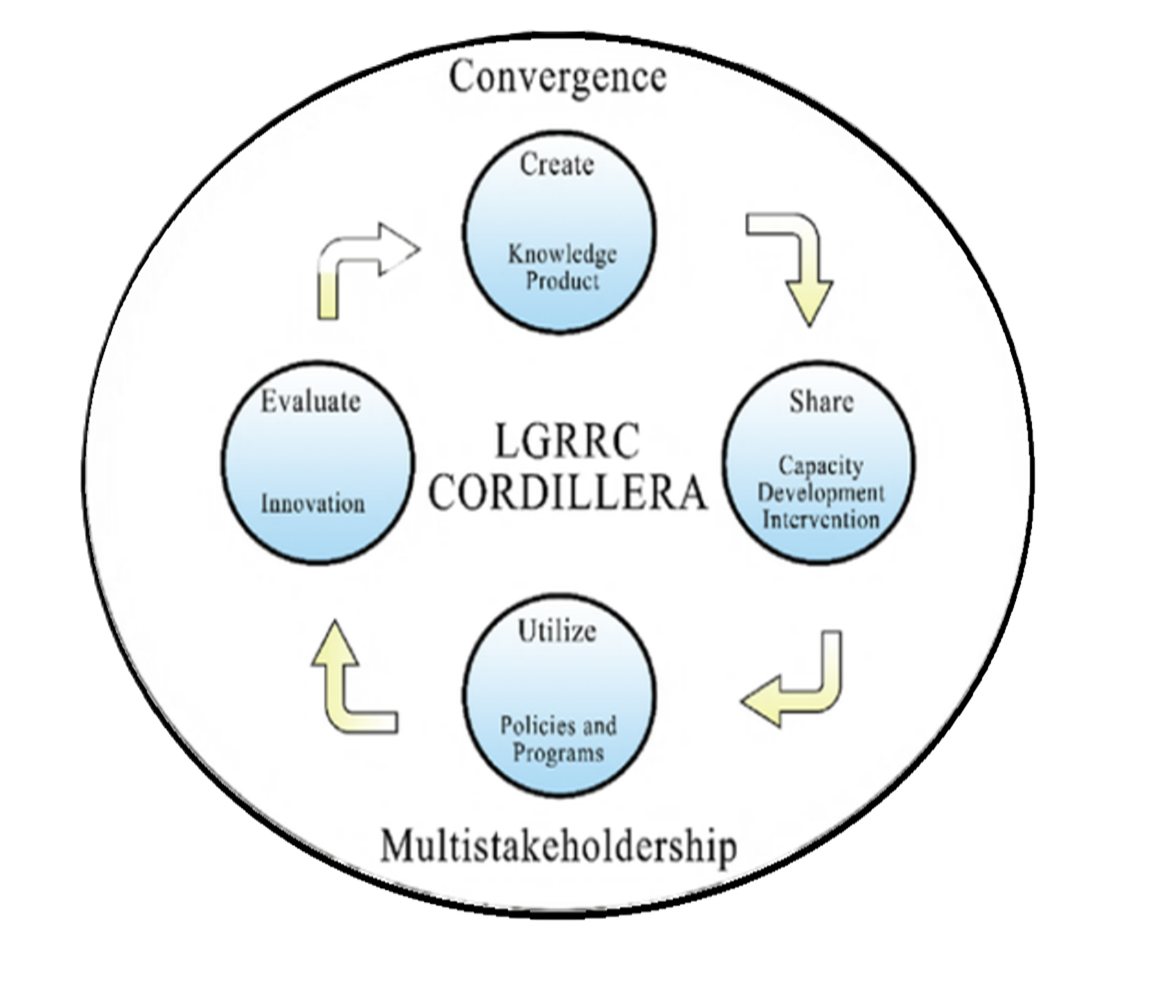
| Create | Share | Utilize | Evaluate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Management(Process) | Platform | Policies and Programs | Innovation |
| Problem Statement | Quad Media, Fora, Face to Face | Policy Development and implementation | Customer Satisfactory Survey |
| Data Collections | Process | Module Development and implementation | Exit Conference |
The acquisition, storage, retrieval, creation, sharing, use, application, and review of a group or organization's explicit and tacit knowledge in a systematic manner to achieve organizational goals. Ultimately, it is about getting the right knowledge to the right people at the right time. But Knowledge Management is not just for information in its various physical forms, but also for tacit knowledge which is intangible and resides as the intellectual capital of individual experts and practitioners. Hence, KM is also about connecting those who know with those who need to know.
For Local Governance Knowledge Management (LG KM) to reflect and respond
to the true knowledge needs and processes of the LG sector, LG KM needs to
involve the key players and stakeholders in participatory local governance. The
essence of multi-stakeholdership is ensuring that these stakeholders
collectively articulate policies in building a culture and system to encourage
better management and sharing of LG knowledge toward excellence in LG. As
such, multiple stakeholders are part of and have “co-ownership” of the KM
system or knowledge community.
Multi-stakeholdership also represents a paradigm shift in DILG's role in local
governance—from supervision and control to that of catalyst and facilitator in
promoting excellence in local governance. In pursuit of its evolving role toward
intra- and inter-sector collaboration for LG KM, for instance, the DILG could take
the lead in establishing these multi-stakeholder mechanisms in overseeing the
KM programs in the sector such as the Local Governance Regional Resource
Center (LGRRC).
These stakeholders include officials, technical personnel, experts, and practitioners of national government agencies, LGUs, NGOs/CSOs, donor organizations, service providers, academic institutions, national, local, and alternative media, think tanks, and research institutions.
By nature, LG KM is a big concept. The value proposition is an ideal that all
stakeholders agree with and are prepared to support and commit its resources
to. As such, the concept of LG KM is a convergence mechanism and rallying
point for many stakeholders to partner together.
On an operational level, LG KM can be a convergence mechanism for various
LG capacity-building initiatives from various levels, institutions, and sectors of
society.
Finally, LG KM can be a convergence mechanism that establishes linkages among various institutions and their resources and makes it possible for unconnected and under-served groups to have access to information and knowledge.
Data management is the LGRRC’s process of generating data and transforming them into meaningful information that can be used by the organization to achieve its accountability, performance, and learning objectives.
The Center for Collaborative Governance Initiative (CCGI) is a joint effort
between the DILG-CAR and its MSAC members to promote effective and
inclusive governance in the Cordillera Administrative Region. This initiative
recognizes that effective governance requires collaboration and partnership
between different sectors and stakeholders, including civil society groups, non
governmental organizations, people's organizations, the private sector, and
other government agencies.
Through the Center for Collaborative Governance Initiative, the DILG-CAR and
its MSAC members work together to identify and address local governance
issues and challenges in the region. The initiative aims to promote
transparency, accountability, and participation in local governance processes,
as well as to enhance the capacity of local government units to deliver
responsive and efficient public services. The Center for Collaborative Governance Initiative involves a range of activities
and interventions, including policy dialogues, capacity development initiatives,community engagement and participation, and the development of partnerships
and networks. The initiative is guided by the principles of good governance,
including participation, transparency, accountability, and responsiveness. It is anchored on the Cordilleran of “Binnadang”, which is a Kankana-ey term
for collaboration. It could be also synonymous with the Tagalog word
“Bayanihan” which refers to the spirit of communal unity, work, and cooperation
to achieve a particular goal. This culture reflects the Collaborative Governance
Initiative as an innovative approach to local governance that recognizes the
value of collaboration and partnership between different stakeholders in
promoting effective and inclusive governance in the Cordillera Administrative
Region. By working together, the DILG-CAR and its MSAC members can
contribute to the development of responsive, accountable, and sustainable local
governance systems that benefit all members of the community.
The CLGRRC is a dynamic and interactive knowledge management convergence platform geared towards sustaining excellence in local governance for the happiness of the Cordillerans.
To initiate and pursue innovative and responsive performance management and capacity development for LGUs by engaging with stakeholders through a matino, mahusay at maasahang workforce.